Significance of digital accessibility and inclusivity
Inclusivity and accessibility in the mobile app development process are vital not only from an ethical standpoint but also for expanding market reach and ensuring compliance with various legal requirements. By breaking barriers and focusing on digital accessibility, we empower persons with disabilities and enable them to have equal access to information, products, and services.
According to World Health Organization statistics, as of March, 7th 2023, Approximately 1.3 billion individuals worldwide are experiencing significant disabilities, which constitutes 16% of the global population. In other words, 1 out of every 6 people is affected by some form of substantial disability. Meaning that it is a big segment of potential app users.
Individuals with special needs face multiple challenges when attempting to use mobile applications that are not designed to accommodate their unique requirements. These challenges include difficulties in navigating through app interfaces, understanding and processing content, and interacting with interactive elements like buttons or menus. Moreover, specific disabilities, such as visual, hearing, cognitive, and physical impairments, require tailored solutions to provide a seamless user experience for all.
Guidelines for ensuring digital accessibility
Undoubtedly, numerous documents, treaties, agreements, and guidelines address various aspects of providing equal access to information. For instance, the Marrakesh Treaty specifically focuses on ensuring access to reading materials for individuals with visual and print impairments. In the realm of digital accessibility, developers can reference the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, which were published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), as a valuable resource for optimizing digital content and user experience.
These guidelines cover a wide range of recommendations for making mobile apps more accessible, organized into four key principles: perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust. By following WCAG, mobile app developers can ensure their apps meet the unique needs of users with diverse abilities.
Implementing WCAG in app development
Incorporating the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) into mobile app development processes helps bridge the digital divide, ensuring an equitable experience for all users. With a more extensive understanding of WCAG guidelines, developers can create inclusive applications.
The suggestions encompass a wide range of subjects related to conveying information, such as providing text alternatives, utilizing time-based media, incorporating appropriate use of color, allowing for pausing, facilitating smooth navigation, employing gestures, and much more.
Seamlessly incorporating the WCAG guidelines into the mobile app development process demands a comprehensive understanding of each principle, coupled with a commitment to prioritizing accessibility. Key steps in achieving this include:
- Establishing accessibility as a core value from the very beginning of the development process.
- Communicating clear instructions to the design and development teams, ensuring that accessible design practices form the backbone of the project.
- Performing regular accessibility audits throughout the development, effectively identifying and addressing potential issues before they solidify in the final product.
- Guaranteeing that all multimedia content, including images, videos, and audio, is made accessible—by providing Alt text for images and captions for videos, for instance.
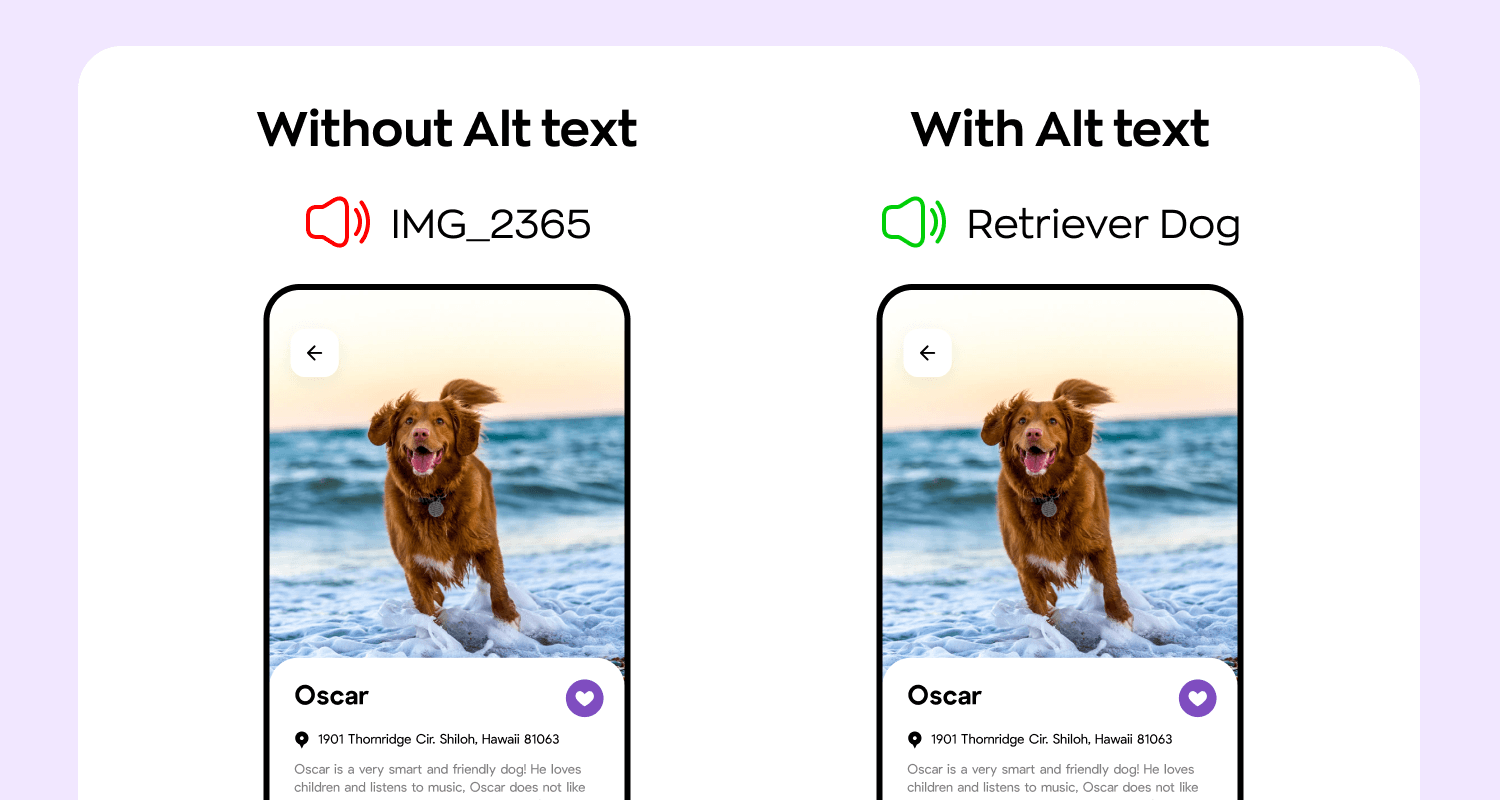
Screen reader will read a file’s name instead of what is depicted on the image without an Alt text
Source: Ronas IT
By integrating WCAG guidelines into app development, developers can create versatile, inclusive, and user-friendly mobile applications that prioritize accessibility and cater to all users, ensuring that digital experiences are equitable and engaging for everyone.
Best practices for accessible user interfaces
An accessible user interface (UI) is the keystone of an inclusive user experience. No matter how feature-rich an app may be, if the UI is not designed to be accessible, it inadvertently excludes a significant portion of potential users. In this section, we will explore some best practices for creating accessible UI designs in mobile apps. To achieve a successfully accessible UI, consider the following best practices:
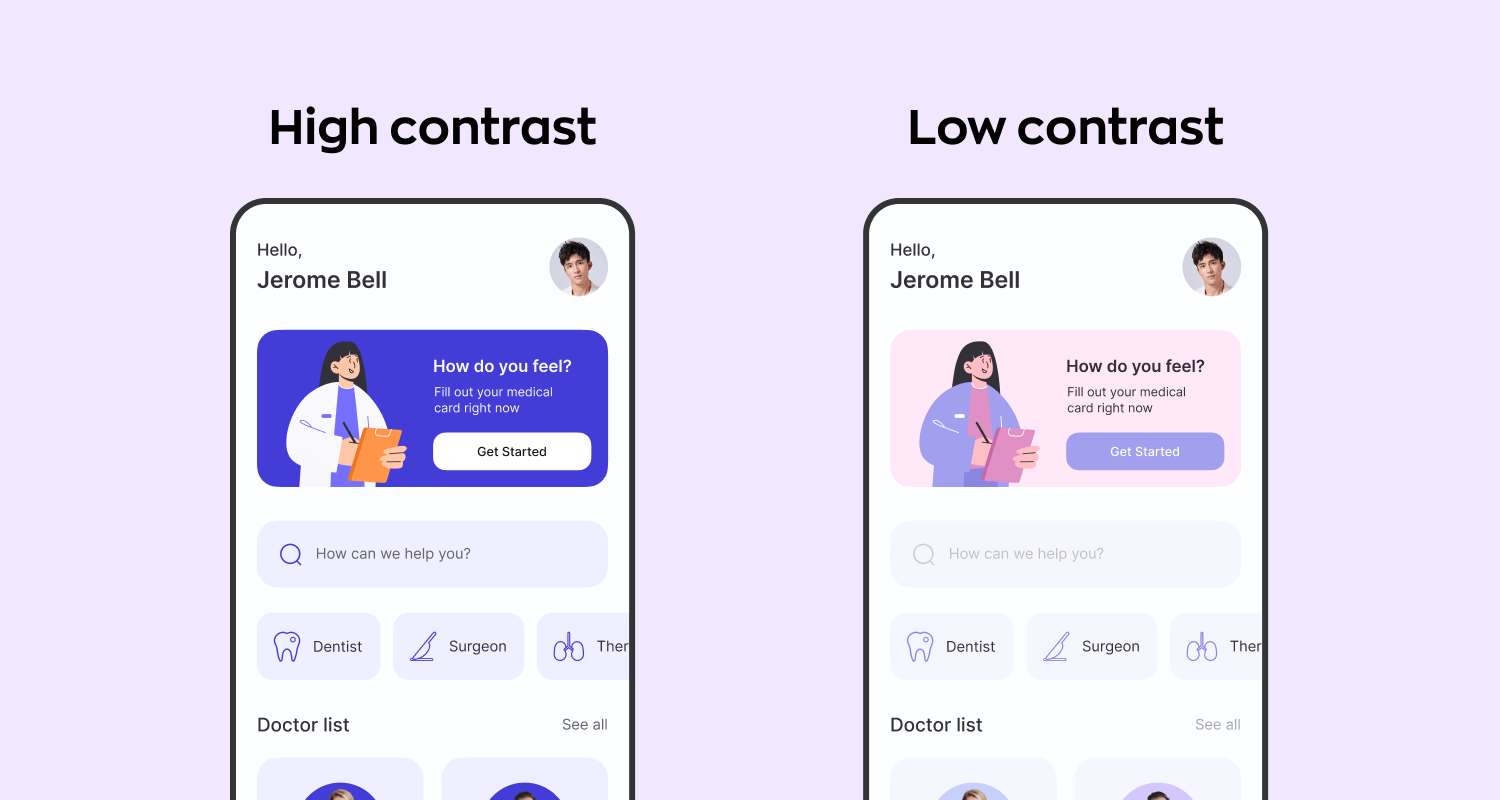
- Optimal color contrast. Make sure that elements within the app are easily distinguishable and visually appealing by using colors with appropriate contrast ratios. This enhances the visibility of text and interactive components, particularly for individuals with vision impairments.
Difference in the readability of images of different contrast
Source: Ronas IT
- Resizable text and adaptable layouts. Accommodate users of varying visual acuity by designing text and layouts that can be resized and adapted to different screen sizes and device orientations.
- Versatile interaction methods. Ensure that all UI elements, including buttons, links, and form fields, are accessible and functional through various input methods like touch, keyboard, and voice commands. This offers flexibility to users with different input preferences or limitations.
- Clear instructions and feedback. Assist users in navigating your app and completing tasks by providing clear instructions, cues, and feedback. This includes informative labels, helpful error messages, and consistent navigation patterns that allow users to easily locate and understand app functions. Offering comprehensive guidance not only aids users with cognitive impairments but also creates a more user-friendly experience for all.
- ARIA landmarks and roles. Implement Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) landmarks and roles to make it easier for assistive technologies to understand and interpret the app’s structure and components. This aids users who rely on screen readers or other assistive tools in navigating the app more efficiently.
- Captioning and transcripts for multimedia. Provide captions and transcripts for all audio and video content within the app. This ensures that users with hearing impairments can access and understand multimedia content as effectively as those without such limitations.
- Customizable user experience. Offer options to tailor the app’s appearance, such as adjustable color schemes and font sizes, to meet individual users’ needs and preferences. This empowers users to create their preferred experience, enhancing accessibility and overall satisfaction.
- Regular accessibility updates and testing. Perform regular audits and updates to ensure continued compliance with accessibility guidelines and standards. Set up a testing routine that includes users with varying abilities to identify and address any issues that may arise.
By implementing these practices, you can create an inclusive, engaging, and user-friendly mobile app that prioritizes accessibility. Adopting guidelines and techniques ensures that mobile apps consider users of all abilities, creating a more inclusive digital world.
Advanced technologies for enhancing accessibility
Emerging technologies offer new opportunities to make mobile apps even more accessible and inclusive. Examples of such technologies include:
- Voice recognition to allow users to control apps using speech commands
- Text-to-speech outputs to convert on-screen text into audible speech, benefiting those with visual or cognitive impairments
- Haptic feedback to offer tactile responses through vibrations, which can enhance accessibility for individuals with hearing or visual impairments
- Eye-tracking to allow users with limited motor control to interact with apps using gaze control
- AI-generated image descriptions to provide contextual information about images for visually impaired users
- Personalized recommendations to offer tailored content to users with cognitive or learning disabilities
By exploring and incorporating advanced technologies like these, developers can further enhance the accessibility of their mobile applications.
To ensure an app is truly accessible and inclusive, it would be great to involve users with disabilities throughout the development process. By including them in user testing and gathering feedback on app design and functionality, developers can identify potential barriers and iterate on the app design accordingly. Involving users with special needs also promotes a sense of ownership and empowerment, giving them a voice in shaping the final product and ensuring it meets their specific needs.
Success stories and case studies
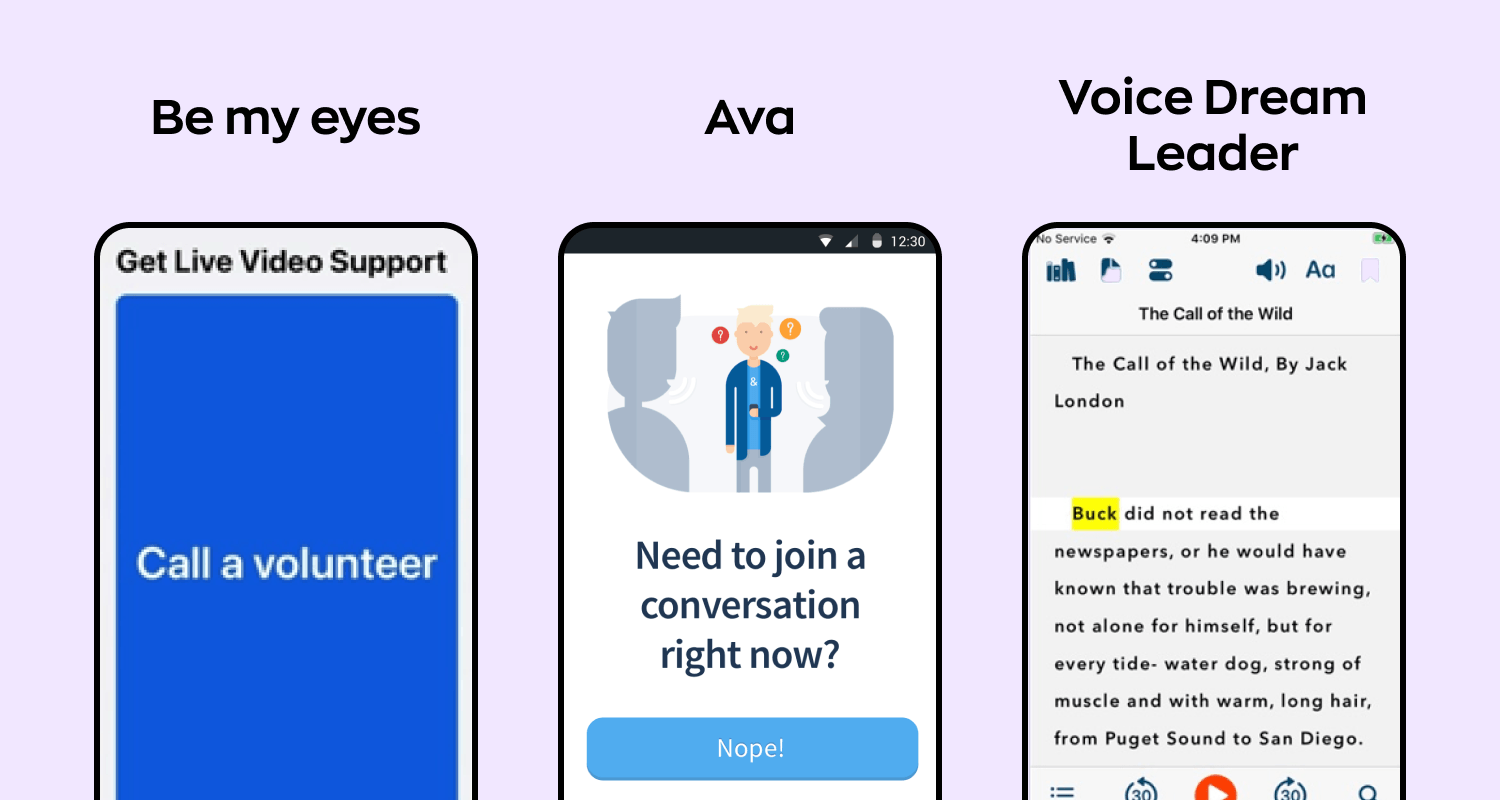
Screens of accessible apps: Be my eyes, Ava, Voice dream reader
Source: Ronas IT
Many mobile apps have effectively implemented accessibility features, benefiting users with disabilities and gaining recognition for their inclusive designs. Some notable examples include:
- Be my eyes. This innovative mobile app connects visually impaired users with sighted volunteers, assisting with daily tasks that require visual guidance. Be My Eyes leverages advanced technologies, including OpenAI’s revolutionary GPT-4, to provide round-the-clock support for its users.
- Ava. Designed to empower individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing, Ava delivers real-time audio captions by seamlessly converting spoken words into written text. This enhances communication, making it more accessible and inclusive for users with hearing impairments.
- Voice dream reader. A comprehensive text-to-speech app, Voice Dream Reader provides customizable settings that cater to users with visual or cognitive impairments. The app promotes greater engagement with written content in various formats and enables users to experience literature more independently and enjoyably.
These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of certain strategies in creating accessible mobile applications. They prioritize accessibility from the very beginning of the app development process. The apps utilize advanced technologies, such as voice recognition and text-to-speech, to enhance the app’s functionality for users with disabilities. Lastly, these examples directly involve users with disabilities in user testing, allowing their feedback to influence and refine the app design and features.
By placing an emphasis on accessibility and inclusivity, these apps have made a significant impact on the lives of users with disabilities by providing them with greater independence, autonomy, and access to information and services. Additionally, these apps have received positive reception and recognition from the broader public and the tech industry, demonstrating the value and importance of inclusive app design.
Conclusion
Creating accessible and inclusive mobile apps not only benefits users with disabilities but also has positive effects on the business side, such as reaching wider audiences and complying with legal requirements. Moreover, app developers and organizations can gain recognition for their inclusive designs and enhance brand reputation.
There is much potential for growth and improvement in mobile app accessibility and inclusivity. By implementing WCAG guidelines, embracing advanced technologies, involving users with disabilities in development, and learning from successful examples, companies can take the necessary steps to create truly accessible and inclusive mobile applications that empower users with disabilities and contribute to a more equitable digital world.
Check out the Ronas IT blog to read about top modern technologies in app development.